Life cycle of active objects
This document describes the life cycle of an active objet.
The diagram illustrates the life-cycle of an active object.
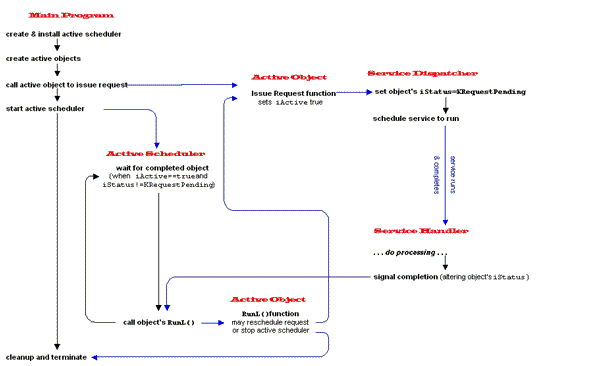
Figure: Flow diagram showing the life cycle of an active object
Procedural flow follows the black arrows; control is transferred along the blue links, as follows:
the main program creates and installs an active scheduler
active objects are created; their constructors ensure that every active object is added to the active scheduler (which keeps a reference to the object in its queue)
an active object is called to issue an initial request. This sets the object's
iActivetrue (indicating a request was issued but not yet completed) and schedules the underlying service, which sets the object'siStatustoKRequestPending. (If this step is omitted, no service will be requested, so no handler will be invoked and hence the active scheduler will wait forever in its loop, never calling any object'sRunL())the active scheduler is started. This now takes over; control is only returned to the main program for termination when the active scheduler is stopped
when a requested service completes, it's handler terminates by signaling service completion; this alters the associated active object's
iStatuswhen any service handler signals completion, the active scheduler tests each object in its queues for one with
iActivetrue (request not completed) andiStatusnot set toKRequestPending(i.e. the request has been handled)if the active scheduler finds an object with the above conditions, it sets
iActivefalse and calls the object'sRunL()the
RunL()may reschedule the request (so that the handler is again invoked when the requested service completes and the cycle continues.) or may stop the active scheduler, returning control to the main program for termination.