SendAs Server
This section provides detailed description of the SendAs Server functions and how the SendAs Server processes the client request.
SendAs Server process and data flow
The following figure details the processes and data flow with SendAs Server.
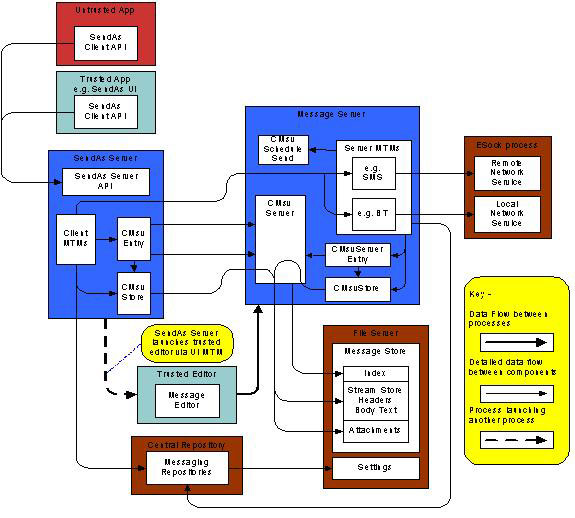
Figure: SendAs Server process and data flow
SendAs Server functionality
The following sections give detailed information about the SendAs sever functionality:
Creating a SendAs message
Client applications can create a message of a
given type that supports SendAs only in the Drafts folder of the message store.
It uses RSendAsMessage::Create() to create the message.
An MTM can specify its support of SendAs for a message type in the following
two ways:
The message type can set the MTM_CAPABILITIES::send_capability resource in its resource file. This allows the Message Server to know whether the message type supports SendAs without loading its MTMs.
If the MTM does not declare whether it supports SendAs in its resource file, the Message Server loads the MTM and queries if it supports the KUidMtmQueryCanSendMsg capability.
Modifying a SendAs message
Client applications can
modify a message created by the RSendAsMessage::Create() method.
After sending the request, client applications can no longer modify the message.
They can add the following message parts, if supported by the message type.
Body text
Attachment
BIO type
Recipients—address, alias and type. For example, To, Cc or Bcc.
Subject
Sending a SendAs Message
When a client application requests to send a message, it must specify whether SendAs must get confirmation from the user to send the message or not.
If a client application that requests a unconfirmed send is not trusted with the capabilities specified by the Server MTM of the given message type, the SendAs Server automatically performs a confirmed send.
For a confirmed send, the SendAs Server uses the UI MTM for the message type to confirm the send request by querying the phone user. If the send is confirmed by the phone user, the SendAs Server moves the message to Outbox and sends the message. If the send is refused, then the message remains in the Drafts folder and the Send-As Server fails the send request.
After the message send is initiated, the Server MTM for the message type takes responsibility of the message. For successful and unsuccessful sends, the Server MTM decides to which folder the message must be moved to. It also governs the rescheduling policy for a failed send request.
A client application can obtain progress for both types of send requests. Any failures associated with the send are reported back to the client application through this progress information. The progress information also provides a send state. For example, message waiting to be sent, sending, message sent, or message send failed.
Launching an editor for a message type
The SendAs Server allows client applications to launch an editor for a specified message type that supports SendAs. After creating a message, a client application can request to launch the appropriate editor. It can launch the editor in two ways: a fire-and-forget launch or a launch and wait. With the fire-and-forget launch, the client application is not notified when an editor is closed. The launch and wait notifies the client application when an editor closes.
After the editor is launched, the SendAs Server is no longer responsible for that message, the editor takes the responsibility. The message editors are applications that are trusted with the required capabilities to modify and send messages of that type. They communicate directly with the Message Server using the Message Server APIs.
Querying the message type registry
The SendAs Server provides several APIs to allow client applications to query the message type registry. The following are the available queries:
List the registered message types that support a specified set of message capabilities. For example, amount of body text allowed, attachments supported and so on.
Obtain the available account names for a specified message type
Get the localised human readable name for a specified message type that supports SendAs.
Note: Message types that have no accounts or invalid accounts are not listed. Validation is done by SendAs querying whether the UI MTM supports validation of the accounts. If the UI MTM does not support validation, all accounts are assumed to be valid. If the UI MTM supports the verification, then the list of service IDs is passed to
InvokeSyncFunctionL using the KMtmUiFunctionValidateService command.The SendAs Server allows client applications only to query the message type registry about message types that support SendAs. Other message types are ignored.